I. Job 기본 개념
· 배치 계층 구조의 가장 상위에 있는 개념, 하나의 배치 작업을 의미한다.
- "API 서버의 접속 로그 데이터를 통계 서버로 옮기는 배치", Job 자체를 의미
· Job Configuration을 통해 생성되는 객체 단위,
배치 작업을 어떻게 구성하고 실행할 것인지 전체적으로 설정하고 명세해 놓은 객체
· Job을 구성하기 위한 최상위 인터페이스, 스프링 배치의 기본 구현체 제공.
· 여러 Step을 포함하고 있는 컨테이너로서 반드시 한개 이상의 Step으로 구성해야함.
@ 컨테이너란?
애플리케이션을 실행하는 데 필요한 모든 요소(코드, 라이브러리, 설정 파일 등)를 하나로 묶어 경량화된 실행 환경을 제공하는 기술
II. Job 기본 구현체
· SimpleJob(Step을 포함)
- 순차적으로 Step을 실행시키는 Job
- 모든 Job에서 유용하게 사용할 수 있는 표준 기능을 갖고 있음.
· FlowJob(Step을 포함 + Flow 객체 포함)
- 특정한 조건과 흐름에 따라 Step을 구성하여 실행시키는 Job
- Flow 객체를 실행시켜서 작업을 진행함.
III. Job 동작 원리
JobParameters -> JobLauncher -> run(job, parameters)
Job -> execute() -> Steps -> Step
↑
Job 실행메서드 Job void excute(JobExecution)
↑
AbstractJob
name : Job 이름
restartable : 재시작 여부 : 기본값은 true
JobRepository : 메타데이터 저장소
JobExecutionListener : Job 이벤트 리스너
JobParametersIncrementer : JobParameter 증가기
JobParametersValidator : JobParameter 검증기
SimpleStepHandler : Step 실행 핸들러
↑
| SimpleJob | FlowJob |
| steps | Flow |
@ Job 구조 디버깅 모드로 따라가보기.
JobConfiguration.java(잡 기본 구성 소스 작성)
package io.springbatch.springbatchseulgae;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Step;
import org.springframework.batch.core.StepContribution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.scope.context.ChunkContext;
import org.springframework.batch.core.step.tasklet.Tasklet;
import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JobConfiguration {
private final JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
private final StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Job job() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("job")
.start(step1())
.next(step2())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step step1() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1")
.tasklet(new Tasklet() {
@Override
public RepeatStatus execute(StepContribution stepContribution, ChunkContext chunkContext) throws Exception {
System.out.println("step1 was executed");
return RepeatStatus.FINISHED;
}
})
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step step2() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step2")
.tasklet(new Tasklet() {
@Override
public RepeatStatus execute(StepContribution stepContribution, ChunkContext chunkContext) throws Exception {
System.out.println("step2 was executed");
return RepeatStatus.FINISHED;
}
})
.build();
}
}
작성한 Job 메서드를 기준으로 디버깅 모드해서 따라가면
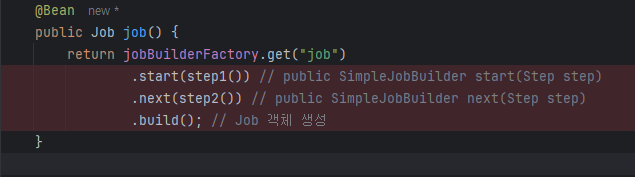
Job에 Ctrl + Alt + B 누르면 Choose Implementation of Job을 볼 수 있음.

1. JobBuilder 호출
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.batch.core.job.builder;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Step;
import org.springframework.batch.core.job.flow.Flow;
public class JobBuilder extends JobBuilderHelper<JobBuilder> {
public JobBuilder(String name) {
super(name);
}
public SimpleJobBuilder start(Step step) {
return (new SimpleJobBuilder(this)).start(step);
}
public JobFlowBuilder start(Flow flow) {
return (new FlowJobBuilder(this)).start(flow);
}
public JobFlowBuilder flow(Step step) {
return (new FlowJobBuilder(this)).start(step);
}
}
2. 요안의 SimpleJobBuilder 클래스 호출한다.
열어보면 SimpleJob이라는 객체를 생성하고, SimpleJobBuilder 클래스의 start 메서드를 호출하는데 구조를 살펴보면
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.batch.core.job.builder;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Step;
import org.springframework.batch.core.job.SimpleJob;
import org.springframework.batch.core.job.flow.JobExecutionDecider;
import org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class SimpleJobBuilder extends JobBuilderHelper<SimpleJobBuilder> {
private List<Step> steps = new ArrayList();
private JobFlowBuilder builder;
public SimpleJobBuilder(JobBuilderHelper<?> parent) {
super(parent);
}
public Job build() {
if (this.builder != null) {
return ((FlowJobBuilder)this.builder.end()).build();
} else {
SimpleJob job = new SimpleJob(this.getName());
super.enhance(job);
job.setSteps(this.steps);
try {
job.afterPropertiesSet();
return job;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new JobBuilderException(e);
}
}
}
public SimpleJobBuilder start(Step step) {
if (this.steps.isEmpty()) {
this.steps.add(step);
} else {
this.steps.set(0, step);
}
return this;
}
public FlowBuilder.TransitionBuilder<FlowJobBuilder> on(String pattern) {
Assert.state(this.steps.size() > 0, "You have to start a job with a step");
for(Step step : this.steps) {
if (this.builder == null) {
this.builder = new JobFlowBuilder(new FlowJobBuilder(this), step);
} else {
this.builder.next(step);
}
}
return this.builder.on(pattern);
}
public JobFlowBuilder start(JobExecutionDecider decider) {
if (this.builder == null) {
this.builder = new JobFlowBuilder(new FlowJobBuilder(this), decider);
} else {
this.builder.start(decider);
}
if (!this.steps.isEmpty()) {
this.steps.remove(0);
}
for(Step step : this.steps) {
this.builder.next(step);
}
return this.builder;
}
public JobFlowBuilder next(JobExecutionDecider decider) {
for(Step step : this.steps) {
if (this.builder == null) {
this.builder = new JobFlowBuilder(new FlowJobBuilder(this), step);
} else {
this.builder.next(step);
}
}
if (this.builder == null) {
this.builder = new JobFlowBuilder(new FlowJobBuilder(this), decider);
} else {
this.builder.next(decider);
}
return this.builder;
}
public SimpleJobBuilder next(Step step) {
this.steps.add(step);
return this;
}
public FlowBuilder.SplitBuilder<FlowJobBuilder> split(TaskExecutor executor) {
for(Step step : this.steps) {
if (this.builder == null) {
this.builder = new JobFlowBuilder(new FlowJobBuilder(this), step);
} else {
this.builder.next(step);
}
}
if (this.builder == null) {
this.builder = new JobFlowBuilder(new FlowJobBuilder(this));
}
return this.builder.split(executor);
}
}
3. Step을 저장할 리스트 변수가 선언되어있고

4. 따라서 내려가다보면 Job build() 메서드가 보이는데 여기서 SimpleJob 객체를 생성한다.
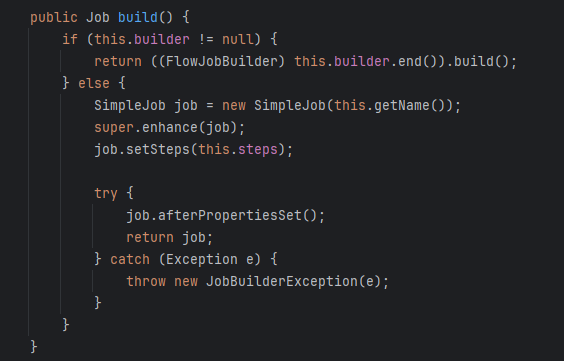
5. 리스트 변수의 선언한 Step을 담아서

5_1. start 메서드를 호출하고 그에 담겨있는 내용은 다음과 같다.

6. SimpleJob의 구조는 다음과 같다.
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.batch.core.job;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.batch.core.BatchStatus;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobInterruptedException;
import org.springframework.batch.core.StartLimitExceededException;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Step;
import org.springframework.batch.core.StepExecution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.repository.JobRestartException;
import org.springframework.batch.core.step.StepLocator;
public class SimpleJob extends AbstractJob {
private List<Step> steps;
public SimpleJob() {
this((String)null);
}
public SimpleJob(String name) {
super(name);
this.steps = new ArrayList();
}
public void setSteps(List<Step> steps) {
this.steps.clear();
this.steps.addAll(steps);
}
public Collection<String> getStepNames() {
List<String> names = new ArrayList();
for(Step step : this.steps) {
names.add(step.getName());
if (step instanceof StepLocator) {
names.addAll(((StepLocator)step).getStepNames());
}
}
return names;
}
public void addStep(Step step) {
this.steps.add(step);
}
public Step getStep(String stepName) {
for(Step step : this.steps) {
if (step.getName().equals(stepName)) {
return step;
}
if (step instanceof StepLocator) {
Step result = ((StepLocator)step).getStep(stepName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
protected void doExecute(JobExecution execution) throws JobInterruptedException, JobRestartException, StartLimitExceededException {
StepExecution stepExecution = null;
for(Step step : this.steps) {
stepExecution = this.handleStep(step, execution);
if (stepExecution.getStatus() != BatchStatus.COMPLETED) {
break;
}
}
if (stepExecution != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Upgrading JobExecution status: " + stepExecution);
}
execution.upgradeStatus(stepExecution.getStatus());
execution.setExitStatus(stepExecution.getExitStatus());
}
}
}
IIII. Job 기본 구성 소스 작성.
package io.springbatch.springbatchseulgae;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Step;
import org.springframework.batch.core.StepContribution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory;
import org.springframework.batch.core.scope.context.ChunkContext;
import org.springframework.batch.core.step.tasklet.Tasklet;
import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JobConfiguration {
private final JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
private final StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Job job() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("job")
.start(step1())
.next(step2())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step step1() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1")
.tasklet(new Tasklet() {
@Override
public RepeatStatus execute(StepContribution stepContribution, ChunkContext chunkContext) throws Exception {
System.out.println("step1 was executed");
return RepeatStatus.FINISHED;
}
})
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step step2() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step2")
.tasklet(new Tasklet() {
@Override
public RepeatStatus execute(StepContribution stepContribution, ChunkContext chunkContext) throws Exception {
System.out.println("step2 was executed");
return RepeatStatus.FINISHED;
}
})
.build();
}
}
'Back-End > SpringBatch' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Batch 시작 - DB 스키마 생성(2) (0) | 2025.04.20 |
|---|---|
| Spring Batch 시작 - DB 스키마 생성(1) (1) | 2025.04.20 |
| SpringBatch Hello Spring Batch 시작하기 (0) | 2025.04.20 |
| Spring Batch 개요 (0) | 2025.04.19 |



